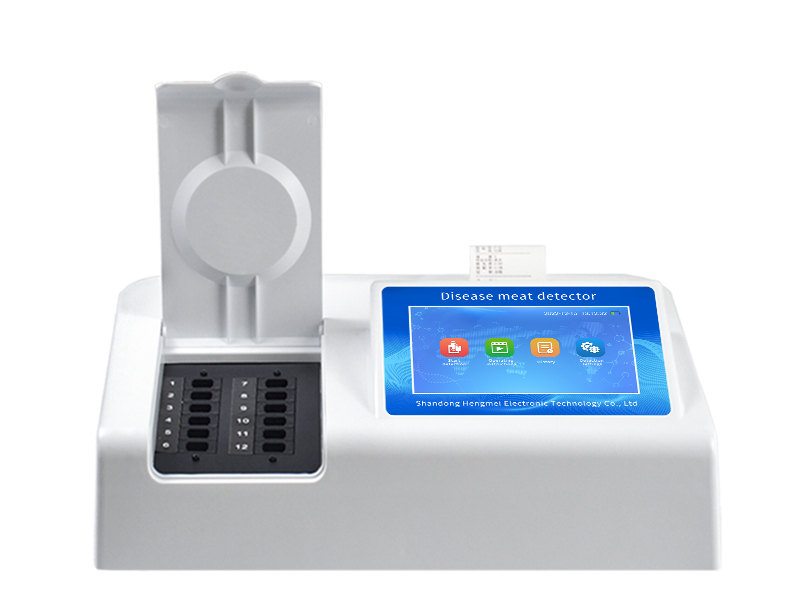
The Diseased Meat Detector achieves on-site rapid screening by compressing detection time to within 15 minutes through integrated design and intelligent algorithms, making it a critical tool for meat food safety supervision.

I. Analysis of Technical Principles and Core Architecture
Multi-channel Joint Detection
The detector employs spectrophotometry to simultaneously detect characteristic indicators of diseased meat:
Sample Pre-treatment: Target substances are extracted via buffer solution, adapting to different meat matrices.
Colorimetric Reaction: Specific reagents are added for different indicators (e.g., o-phthalaldehyde for histamine).
Optical Signal Acquisition: A 12-channel rotating colorimetric cell design with 4-wavelength LED light sources enables synchronous detection.
Data Analysis: The ARM Cortex-A7 processor runs calibration algorithms to eliminate interference from meat matrices.
Core Instrument Parameters
Detection Items: Diseased meat, histamine, volatile base nitrogen, covering all indicators specified in GB 2707-2016 standards.
Detection Time: 15–30 minutes for 12 samples, improving efficiency by over 16 times.
Precision: CV ≤ 3% (relative standard deviation), complying with NY/T 1896-2010 detection standards.
Data Transmission: 4G/WiFi/Ethernet connectivity, supporting integration with food safety supervision platforms.
Power Management: Lithium battery provides 8 hours of endurance, meeting all-weather field operation requirements.
Display System: 8-inch touchscreen supporting gesture controls and data curve display.
II. Industry Pain Points and the Detector’s Solutions
Limitations of Traditional Detection Methods
Difficult Site Selection: High cost of fixed monitoring stations limits coverage across meat circulation nodes.
Data Latency: Laboratory analysis prolongs the circulation time of problematic meat.
High Operational Threshold: Grassroots personnel struggle with complex instrument operation.
High Maintenance Costs: Expenses for consumable replacement and calibration are significant.
Innovative Breakthroughs of the Diseased Meat Detector
Mobile Monitoring Capability: Weighs <5 kg with a portable design for easy carrying.
Real-time Data Transmission: Synchronizes data to food safety supervision platforms via 4G.
User-friendly Operation: Touchscreen interface guides users through a 3-step detection process.
Low-cost Maintenance: Annual consumable costs are less than 1/20 of those of traditional methods.
III. Cross-industry Application Scenarios
Regulatory Enforcement: Random inspections in farmers’ markets, surprise checks at catering establishments, and special campaigns during festivals.
Food Production: Raw material intake testing, production process monitoring, and finished product screening.
Research and Education: Studies on meat spoilage mechanisms, validation of new preservation technologies, and student实验training.
Emergency Response: Handling food safety incidents, ensuring security during major events, and responding to public opinion crises.
Address of this article:http://www.hmfoodtesting.com/article/154.html


 Current
location:
Current
location: